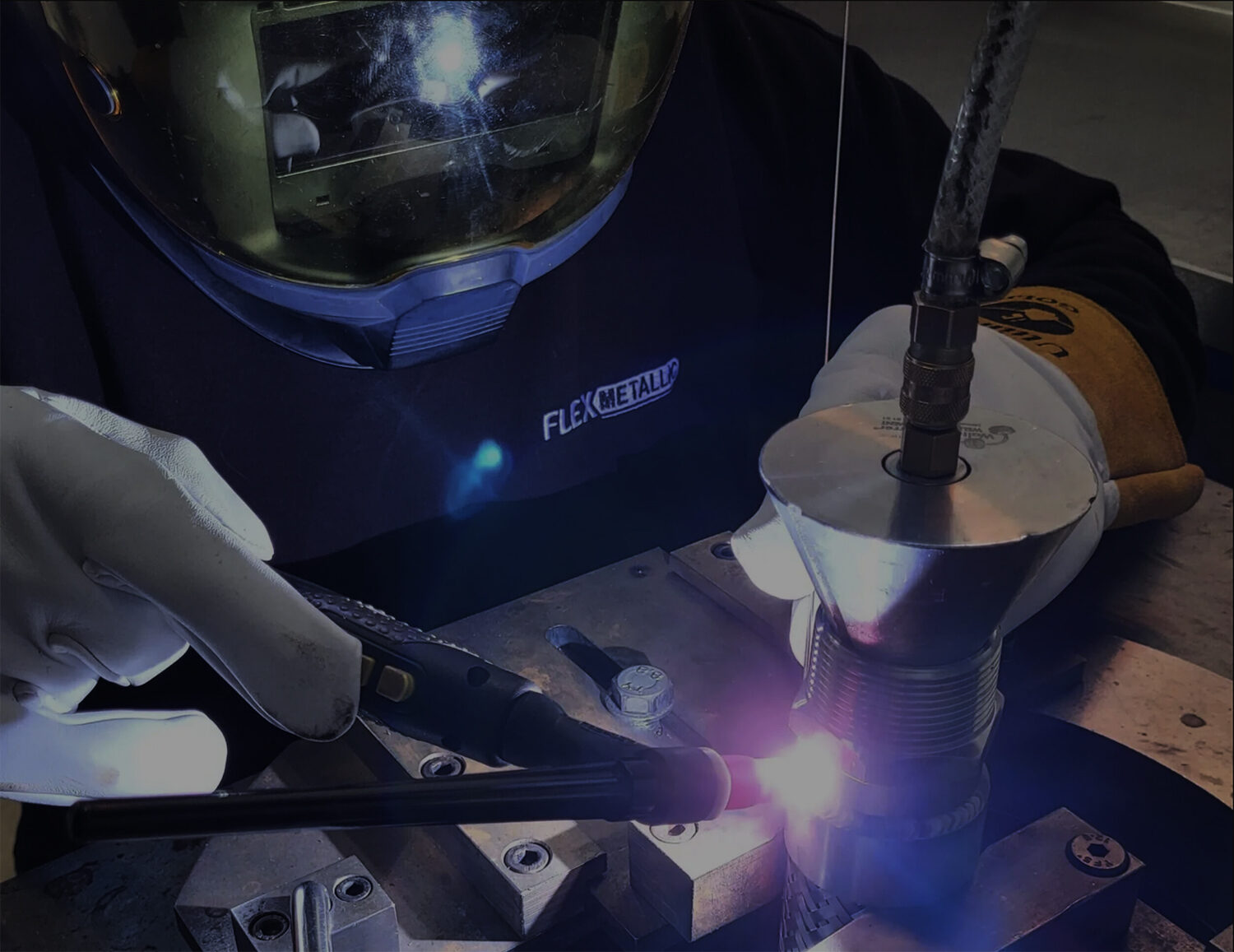


The FMI welding process
At Flexmetallic Industries we manufacture our metal hose assemblies using the TIG welding method.
Argon is used as a shielding gas in Welding Systems. During the welding, process metals are exposed to temperatures of upwards of 7000°F. At these temperatures, most metals become liquid, which allows the formation of the weld.
Argon is used to protect the molten pool of metal against elements in the Atmosphere including Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Hydrogen. These elements cause reactions with the liquid weld pool, such as porosity and increased weld spatter. Argon also plays an important role in maintaining Arc stability, which leads to increased weld penetration, better filler wire transfer, and better weld appearance.
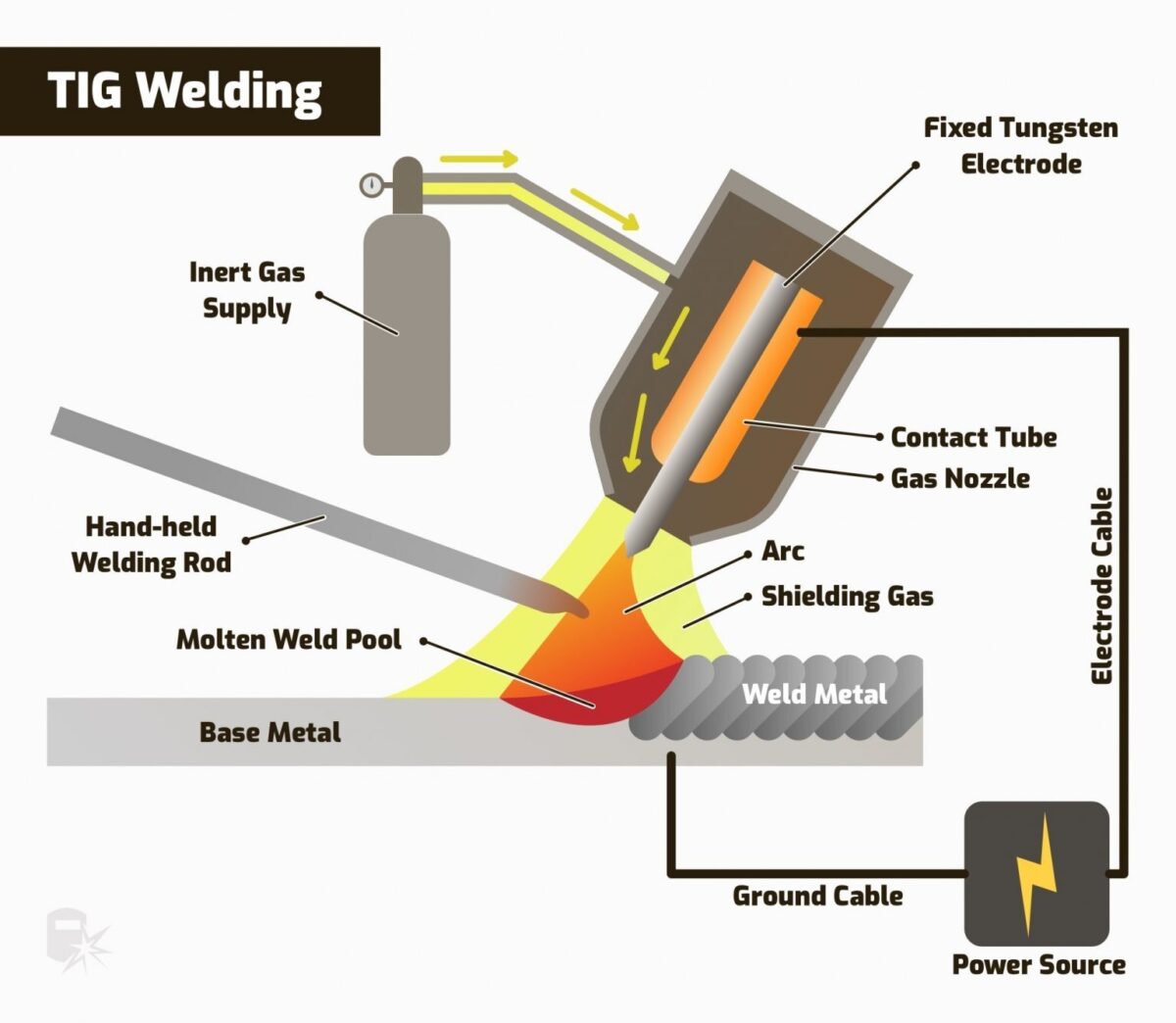
Argon Backed Welding Method
Welding method causes less damage to surface areas.
Eliminates heat damage, that result in burrs and resultant surface damage.
Decreases the risk of corrosion.
Decreases the risk of leaks.
Welding & Assembly Techniques
The manufacturing of flexible corrugated metal hose assemblies involves precision welding and assembly techniques to ensure reliability and performance. Automated and manual welding processes are employed to join the corrugated metal tubing and end fittings securely. Additionally, stringent quality control measures are implemented throughout the assembly process to maintain consistency and integrity.
- Butt Welding: Butt welding is a common technique used to join sections of corrugated metal hose during manufacture. This process involves aligning the ends of the hose sections and applying heat to fuse them together, creating a seamless connection. Butt welding ensures a strong, leak-free joint and maintains the structural integrity of the hose.
- Fillet Welding: Fillet welding is employed to attach end fittings, such as flanges or threaded ends to corrugated metal hoses. This technique involves welding the fitting directly to the hose ends, providing a secure and reliable connection. Fillet welding ensures proper alignment and sealing between the hose assembly and connected equipment.
- End Fittings: Flexible corrugated metal hose assemblies are terminated with end fittings that facilitate connection to other components within the system. These fittings, available in various configurations such as threaded, flanged, or tube connections. They ensure a secure and leak-free interface, maintaining system integrity.
- Reinforcement Layers (Optional): In applications requiring additional reinforcement to withstand higher pressures or protect against abrasion, the corrugated metal hose may feature additional outer layers of braiding or a procoil wire armour. These reinforcement layers, typically made from stainless steel or interlocked metal strips, enhance mechanical strength, durability and also protection from external damage.
Temperature Ranges and Working Pressures
Temperature Range: Corrugated flexible metal hose assemblies exhibit excellent temperature resistance, allowing them to operate effectively across a wide range of temperatures. The minimum and maximum temperature ranges depend on factors such as the specific materials used in construction and the application requirements. However, as a general guideline, these assemblies can typically withstand temperatures ranging from -200°C to +600°C (-328°F to +1112°F), making them suitable for both cryogenic and high-temperature applications.
Working Pressures: The working pressures of corrugated flexible metal hose assemblies vary depending on factors such as the diameter of the hose, the material of construction, and the application conditions. However, these assemblies are engineered to withstand a wide range of pressures encountered in industrial environments. Common working pressures for standard assemblies range from vacuum to several thousand psi (pounds per square inch), with specialized designs available for higher-pressure applications.
Certification
The Flexmetallic welding team is certified to weld hoses to both BS EN 9606-1 and ASME IX qualifications depending on customers’ requirements. (Certificates available on request). We adhere to the rigorous standards set forth by these standards. The ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section IX (ASME IX) code provides guidelines for welding and brazing qualifications, ensuring that the procedures, welders, and welding operators can produce welds of the required quality for their intended application.
Procedure Qualification Records (PQR)
Development
Flexmetallic begins by developing a Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) that outlines the welding process, materials, joint design, preheat and post-weld heat treatment, and other variables.
Testing
A test weld is made following the WPS. This weld is then subjected to various tests (such as tensile tests, bend tests, and impact tests) to ensure it meets the mechanical property requirements.
Documentation
The results are documented in a Procedure Qualification Record (PQR). This record demonstrates that the WPS can produce a weld that meets all required standards.
Welder Performance Qualification (WPQ)
Skill Demonstration: Welders and welding operators must demonstrate their ability to produce sound welds by performing test welds under the conditions specified in the WPS.
Testing
These test welds are evaluated using non-destructive testing methods (such as radiographic or ultrasonic testing) and destructive tests to verify their integrity.
Certification
Successful completion of the tests results in the issuance of a Welder Performance Qualification (WPQ) certificate. This certificate indicates that the welder is qualified to perform welds according to the specified WPS.
Quality Assurance
- Inspection and Testing: Ongoing inspection and testing ensure that the welds continue to meet the required standards. This can include visual inspection, radiographic testing, ultrasonic testing, and other non-destructive examination (NDE) methods.
- Documentation and Traceability: Maintaining detailed records of all procedures, qualifications, and inspections is crucial for traceability and quality assurance.
Staying Current
- Flexmetallic stay current with any updates to the BS EN 9606-1 and ASME IX code and ensure that all procedures and qualifications comply with the latest standards.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular reviews and improvements of welding procedures help in maintaining high standards of quality and efficiency.
- By following these steps, Flexmetallic ensures that our welded hoses are manufactured to the highest standards of safety and reliability, complying with all qualifications. This rigorous approach helps in producing welds that can withstand the demands of their intended applications, ensuring longevity and performance.

Get in touch
It’s time we talked, send a message
Speak to an experienced engineer to discuss your unique requirements